The Computer and its
Components.
This Article will cover
Output Devices:
Compiled by “Md. Farrukh Asif”
Below are some main
computer output devices:
Click Me to Explore
Detailed description of the Computer and its Components.
(Input Units)
A Complete and Detailed Definition with examples of Output
Devices (New Tech based)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Latest Enquiries
Memory Unit (I/O) Devices by Farrukh
The Basic Terminologies of Computer by Md. Farrukh Asif
Generation of Computer by Md. Farrukh Asif
The Evolution of Computer Languages(Part-I) by Md. Farrukh
Asif
The Evolution of Computer Languages(Part-II) by Md. Farrukh
Asif
Computer Network Topologies
By Md. Farrukh Asif
Communication Protocols
by “Md Farrukh Asif”
Basic Computer's Features and Use by Md. Farrukh Asif
Operating System and its Functionality: by Md. Farrukh Asif
Batch OS and Time Sharing OS by Md. Farrukh Asif
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS): Explained Simply
The Wider
Use of Microkernel and its Components in OS
Fundamentals of Computer MCQs with Answers
Previous: Input Devices Next: I/O
Devices
·
Output Units
Output
Devices
The output
device displays the result of the processing of raw data that is entered in the
computer through an input device. There are a number of output devices that
display output in different ways such as text, images, hard copies, and audio
or video.
Some of the
popular output devices are:
1) Monitor
a) CRT Monitor
b) LCD Monitor
c) LED Monitor
d) Plasma Monitor
2) Printer
a) Impact Printers
i) Character Printers
ii) Dot Matrix printers
iii) Daisy Wheel printers
iv) Line printers
v) Drum printers
vi) Chain printers
b) Non-impact printers
i) Laser printers
ii) Inkjet printers
iii) Thermal printers
3) Projector
1. Monitor
The monitor
is the display unit or screen of the computer. It is the main output device
that displays the processed data or information as text, images, audio or
video.
The types of
monitors are given below.
a) CRT Monitor
CRT monitors
are based on the cathode ray tubes. They are like vacuum tubes which produce
images in the form of video signals. Cathode rays tube produces a beam of
electrons through electron guns that strike on the inner phosphorescent surface
of the screen to produce images on the screen. The monitor contains millions of
phosphorus dots of red, green and blue color. These dots start to glow when
struck by electron beams and this phenomenon is called cathodoluminescence.
The main
components of a CRT monitor include the electron gun assembly, deflection plate
assembly, fluorescent screen, glass envelope, and base.The front (outer
surface) of the screen onto which images are produced is called the face plate.
It is made up of fiber optics.
There are
three electron beams that strike the screen: red, green, and blue. So, the
colors that you see on the screen are the blends of red, blue, and green
lights. The magnetic field guides the beams of electrons. Although LCDs have
replaced CRT monitors, the CRT monitors are still used by graphics
professionals because of their color quality.
b) LCD Monitor
The LCD monitor is a flat panel screen that is compact and lightweight as compared to CRT monitors. It is based on liquid crystal display technology which is used in the screens of laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc. An LCD screen comprises two layers of polarized glass with a liquid crystal solution between them. When the light passes through the first layer, an electric current aligns the liquid crystals. The aligned liquid crystals allow a varying level of light to pass through the second layer to create images on the screen.
The LCD
screen has a matrix of pixels that display the image on the screen.Old LCDs had
passive-matrix screens in which individual pixels are controlled by sending a
charge. A few electrical charges could be sent each second which made screens
appear blurry when the images moved quickly on the screen.
Modern LCDs
use active-matrix technology and contain thin film transistors (TFTs) with
capacitors. This technology allows pixels to retain their charge. So, they
don?t make the screen blurry when images move fast on the screen as well as are
more efficient than passive-matrix displays.
c) LED Monitor
The LED monitor is an improved version of an LCD monitor. It also has a flat panel display and uses liquid crystal display technology like LCD monitors. The difference between them lies in the source of light to backlight the display. The LED monitor has many LED panels, and each panel has several LEDsto backlight the display, whereas the LCD monitors use cold cathode fluorescent light to backlight the display. Modern electronic devices such as mobile phones, LED TVs, laptop and computer screens, etc., use an LED display as it not only produces more brilliance and greater light intensity but also consumes less power.
d) Plasma Monitor
The plasma monitor is also a flat panel display that is based on plasma display technology. It has small tiny cells between two glass panels. These cells contain mixtures of noble gases and a small amount of mercury. When voltage is applied, the gas in the cells turns into plasma and emits ultraviolet light that creates images on the screen, i.e., the screen is illuminated by a tiny bit of plasma, a charged gas. Plasma displays are brighter than liquid crystal displays (LCD) and also offer a wider viewing angle than an LCD.
Plasma
monitors provide high resolutions of up to 1920 X 1080, excellent contrast
ratios, wide viewing angles, a high refresh rate, and more. Thus, they offer a
unique viewing experience while watching action movies, sports games, and more.
2. Printer
A printer
produces hard copies of the processed data. It enables the user, to print
images, text or any other information onto the paper.
Based on the
printing mechanism, the printers are of two types: Impact Printers and
Non-impact Printers.
Impact
Printers: They are of two types:
i) Character Printers
ii) Dot Matrix printers
iii) Daisy Wheel printers
iv) Line printers
v) Drum printers
vi) Chain printers
Non-impact
printers: They are of three types:
i) Laser printers
ii) Inkjet printers
iii) Thermal printers
iv) Impact Printer
The impact
printer uses a hammer or print head to print the character or images onto the
paper. The hammer or print head strikes or presses an ink ribbon against the
paper to print characters and images.
Impact printers:
Impact
printers are further divided into two types.
Character
Printers
Line
printers
A) Character
Printers
Character
printer prints a single character at a time or with a single stroke of the
print head or hammer. It does not print one line at a time. Dot Matrix printer
and Daisy Wheel printer are character printers. Today, these printers are not
in much use due to their low speed and because only the text can be printed.
The character printers are of two types, which are as follows:
i) Dot
Matrix Printer
The Dot Matrix
Printer is an impact printer. The characters and images printed by it are the
patterns of dots. These patterns are produced by striking the ink-soaked ribbon
against the paper with a print head. The print head contains pins that produce
a pattern of dots on the paper to form the individual characters. The print
head of a 24-pin dot matrix contains more pins than a 9 pin dot matrix printer,
so it produces more dots which results in better printing of characters. To
produce color output, the black ribbon can be changed with color stripes. The
speed of Dot Matrix printers is around 200-500 characters per second.
ii) Daisy
Wheel Printer
The Daisy Wheel Printer was invented by David S. Lee at Diablo Data Systems.It consists of a wheel or disk that has spokes or extensions and looks like a daisy, so it is named the Daisy Wheel printer. At the end of extensions, molded metal characters are mounted. To print a character the printer rotates the wheel, and when the desired character is on the print location the hammer hits disk and the extension hits the ink ribbon against the paper to create the impression. It cannot be used to print graphics and is often noisy and slow, i.e., the speed is very low around 25-50 characters per second. Due to these drawbacks, these printers have become obsolete.
B) Line
Printers:
Line
printer, which is also as a bar printer, prints one line at a time. It is a
high-speed impact printer as it can print 500 to 3000 lines per minute. Drum
printers and chain printers are examples of line printers.
i) Drum
Printer:
A drum printer is a line printer that is made of a rotating drum to print characters. The drum has circular bands of characters on its surface. It has a separate hammer for each band of characters. When you print, the drum rotates, and when the desired character comes under the hammer, the hammer strikes the ink ribbon against the paper to print characters. The drum rotates at a very high speed and characters are printed by activating the appropriate hammers. Although all the characters are not printed at a time, they are printed at a very high speed. Furthermore, it can print only a predefined style as it has a specific set of characters. These printers are known to be very noisy due to the use of hammering techniques.
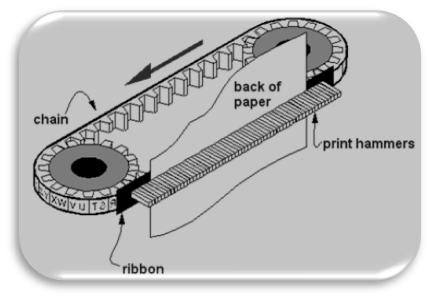
ii) Chain
Printer:
A chain printer is a line printer that uses a rotating chain to print characters. The characters are embossed on the surface of the chain. The chain rotates horizontally around a set of hammers, for each print location one hammer is provided, i.e., the total number of hammers is equal to the total number of print positions.
The chain
rotates at a very high speed and when the desired character comes to the print
location, the corresponding hammer strikes the page against the ribbon and
character on the chain. They can type 500 to 3000 lines per minute. They are
also noisy due to the hammering action.
Non-Impact Printer:
Non-impact
printers don't print characters or images by striking a print head or hammer on
the ink ribbon placed against the paper. They print characters and images
without direct physical contact between the paper and the printing machinery.
These printers can print a complete page at a time, so they are also known as
page printers. The common types of non-impact printers are Laser printers and
Inkjet printers:
i) Laser
Printer:
A laser printer is a non-impact printer that uses a laser beam to print the characters. The laser beam hits the drum, which is a photoreceptor and draws the image on the drum by altering electrical charges on the drum. The drum then rolls in toner, and the charged image on the drum picks the toner. The toner is then printed on the paper using heat and pressure. Once the document is printed, the drum loses the electric charge, and the remaining toner is collected. The laser printers use powdered toner for printing instead of liquid ink and produce quality print objects with a resolution of 600 dots per inch (dpi) or more.
ii) Inkjet
Printer:
The inkjet printer is a non-impact printer that prints images and characters by spraying fine,ionized drops of ink. The print head has tiny nozzles to spray the ink. The printer head moves back and forth and sprays ionized drops of ink on the paper, which is fed through the printer. These drops pass through an electric field that guides the ink onto the paper to print correct images and characters.
An inkjet
printer has cartridges that contain ink. Modern inkjet printers are color
printers that have four cartridges containing different colors: Cyan, Magenta,
Yellow, and Black. It is capable of printing high-quality images with different
colors. It can produce print objects with a resolution of at least 300 dots per
inch (dpi).
3) Projector
A projector is an output device that enables the user to project the output onto a large surface such as a big screen or wall. It can be connected to a computer and similar devices to project their output onto a screen. It uses light and lenses to produce magnified texts, images, and videos. So, it is an ideal output device to give presentations or to teach a large number of people.
Modern
projects (digital projectors) come with multiple input sources such as HDMI
ports for newer equipment and VGA ports that support older devices. Some
projectors are designed to support Wi-Fi and Bluetooth as well. They can be
fixed onto the ceiling, placed on a stand, and more and are frequently used for
classroom teaching, giving presentations, home cinemas, etc.
A digital
projector can be of two types:
Liquid
Crystal Display (LCD) digital projector: This type of digital projector are very popular as
they are lightweight and provide crisp output. An LCD projector uses
transmissive technology to produce output. It allows the light source, which is
a standard lamp, to pass through the three colored liquid crystal light panels.
Some colors pass through the panels and some are blocked by the panels and thus
images are on the screen.
Digital
Light Processing (DLP) digital projector: It has a set of tiny mirrors, a separate mirror
for each pixel of the image and thus provides high-quality images. These
projectors are mostly used in theatres as they fulfill the requirement of
high-quality video output.
Questions Answer Section:
Q. HOW WILL
YOU EXPLAIN MONITOR AND ITS TYPES WITH EXAMPLE IN DETAIL?
A
monitor, in the context of computer hardware, is an output device that displays
visual information. It is an essential component of a computer system, allowing
users to interact with the operating system, applications, and multimedia.
Monitors come in various types and technologies, each with its specific
characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Here's a detailed explanation
of the main types of monitors, along with examples:
1. Cathode Ray Tube
(CRT) Monitors
CRT
monitors were the first type of monitors used in computers and television
screens. They use a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent
screen to create images.
·
How
it works: The electron gun emits a beam of electrons, which are directed and
focused by magnetic fields onto a phosphorescent screen. The screen glows when
hit by the electron beam, creating the image.
·
Characteristics:
CRT monitors are bulky and heavy, have a lower resolution compared to modern
displays, and consume more power. However, they offer good color accuracy and
viewing angles.
·
Example:
Older television sets and computer monitors used in the late 20th century.
2. Liquid Crystal
Display (LCD) Monitors
LCD
monitors use liquid crystals and a backlight to produce images. They have
largely replaced CRT monitors due to their slimmer design and lower power
consumption.
·
How
it works: LCDs consist of liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of
polarizing material. When an electric current is applied, the crystals align to
allow light to pass through, forming images.
·
Characteristics:
LCDs are lightweight, slim, energy-efficient, and have high resolution. They
come in two main types: Twisted Nematic (TN) and In-Plane Switching (IPS), with
IPS offering better color accuracy and viewing angles.
·
Example:
Most modern computer monitors, televisions, and mobile device screens.
3. Light Emitting Diode
(LED) Monitors
LED
monitors are a type of LCD monitor that uses LEDs for backlighting instead of
the traditional cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs).
·
How
it works: LEDs provide backlighting that is more efficient and can produce
better contrast and brightness. The panel technology (TN, IPS, etc.) is the
same as LCD monitors.
·
Characteristics:
LED monitors are more energy-efficient, have a slimmer design, and offer better
color accuracy and brightness than standard LCD monitors.
·
Example:
Modern computer monitors, televisions, and many digital displays.
4. Organic Light
Emitting Diode (OLED) Monitors
OLED
monitors use organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is
applied. Unlike LCDs, OLEDs do not require a backlight, as each pixel produces
its own light.
·
How
it works: Each pixel in an OLED display is an organic compound that emits light
directly when electric current passes through it.
·
Characteristics:
OLED monitors offer excellent color accuracy, high contrast ratios (true
blacks), wide viewing angles, and faster response times. They can also be made
very thin and flexible.
·
Example:
High-end smartphones, televisions, and some high-end computer monitors.
5. Plasma Display Panel
(PDP) Monitors
Plasma
monitors use small cells containing electrically charged ionized gases
(plasmas) to produce images.
·
How
it works: Each cell acts as a small fluorescent light, emitting ultraviolet
light that then excites phosphors to produce visible light.
·
Characteristics:
Plasma monitors offer good color accuracy, wide viewing angles, and good motion
performance. However, they are heavier and consume more power than LCDs and
OLEDs.
·
Example:
Large-screen televisions (common before the widespread adoption of LED and OLED
technologies).
6. Quantum Dot (QLED)
Monitors
·
QLED
monitors use quantum dot technology, which involves nanocrystals that emit
light when illuminated by a light source (such as an LED).
·
How
it works: Quantum dots are tiny semiconductor particles that can emit light of
specific wavelengths when exposed to light. They are used in conjunction with
an LED backlight to enhance color accuracy and brightness.
·
Characteristics:
QLED monitors offer improved color accuracy and brightness over traditional LED
monitors, with better energy efficiency.
·
Example:
High-end televisions and monitors, particularly those marketed as offering
superior color performance.
Comparison of Monitor Types
·
CRT:
Bulky, heavy, good color, high power consumption.
·
LCD:
Slim, lightweight, energy-efficient, good resolution.
·
LED:
Enhanced LCD with better color and efficiency.
·
OLED:
Excellent color, high contrast, wide viewing angles, thin design.
·
Plasma:
Good color and motion, heavier, higher power consumption.
·
QLED:
Improved color and brightness over traditional LED.
Each
monitor type has its specific use cases and target audiences. For instance,
CRTs were widely used until the early 2000s but have been replaced by LCD and
LED monitors due to their superior characteristics. OLED and QLED are among the
latest technologies, offering exceptional image quality for premium devices.
------------------------------------------------------
Q. Define
Printers and their types. also differences between impact and non-impact
printers
Printers
are peripheral devices that produce a physical copy (often referred to as a
"hard copy") of digital documents, images, or other content from a
computer or electronic device. Printers can be classified into two broad
categories based on how they transfer ink or toner to paper: impact and non-impact
printers.
Types of Printers
1. Impact Printers
Impact
printers create an image by physically striking an ink ribbon against the
paper, much like a typewriter. They are generally used for specific
applications where multiple copies of a document are needed simultaneously,
such as in business settings.
·
Dot
Matrix Printers:
These use a print head that moves back and forth or in an up-and-down motion on
the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the
paper, making tiny dots on the paper. Multiple pins in the print head can
produce characters and graphics.
·
Daisy
Wheel Printers: These
work similarly to typewriters, using a rotating disk with pre-formed characters
(the "daisy wheel") that strike the paper through an ink ribbon.
·
Line
Printers: These are
high-speed impact printers that print an entire line at once. They are
typically used in environments that require high-volume printing, like data
centers.
2. Non-Impact Printers
Non-impact
printers do not strike the paper. Instead, they use other technologies to
transfer ink or toner to the paper. These printers are quieter and capable of
producing higher-quality output than impact printers.
·
Inkjet
Printers: These spray
tiny droplets of liquid ink onto the paper. Inkjet printers are popular for
both home and office use because they can produce high-quality text and color
images.
·
Laser
Printers: These use a
laser beam to produce an image on a drum that is then transferred to the paper
using toner (powdered ink). Laser printers are known for their speed,
precision, and high-quality output, especially for text documents.
·
Thermal
Printers: These use
heat to transfer dye onto paper or another medium. There are two main types: direct
thermal printers, which use heat-sensitive paper, and thermal transfer
printers, which use a heat-sensitive ribbon.
·
LED
Printers: Similar to
laser printers but use an array of LEDs to create the image on the drum.
Differences Between Impact and Non-Impact Printers
1.
Printing Mechanism:
o Impact
Printers: Use a mechanical process to physically strike the paper
through an ink ribbon.
o Non-Impact
Printers: Use non-mechanical processes like spraying ink, using
lasers, or thermal transfer.
2.
Noise Level:
o Impact
Printers: Tend to be noisier due to the mechanical striking action.
o Non-Impact
Printers: Generally quieter since there is no physical striking
involved.
3.
Print Quality:
o Impact
Printers: Typically lower print quality, especially for graphics and
images.
o Non-Impact
Printers: Higher print quality, suitable for both text and images.
4.
Speed:
o Impact
Printers: Usually slower, especially for high-quality output.
o Non-Impact
Printers: Often faster, particularly in the case of laser and LED
printers.
5.
Use Cases:
o Impact Printers: Suitable
for environments needing multi-part forms, carbon copies, or continuous
stationery.
o Non-Impact
Printers: Widely used for general-purpose printing, including text,
graphics, and high-quality images.
---------------------------------------
***************************
Share, Like & Comments Please…
***************************











No comments:
Post a Comment